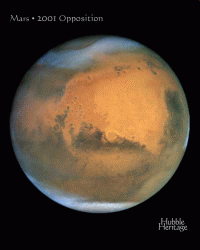
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The NASA-JPL Mars Exploration site overviews of all previous, current, and planned US missions to Mars, with links to project homepages and other information.operational: Perseverance Rover - Ingenuity HelicopterNASA's fifth Mars rover, Mars 2020 Perseverance Rover, launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida on July 30, 2020, is a car-sized vehicle that has been exploring the Jezero crater on Mars since landing there on February 18, 2021. Perseverance is powered by a radioisotope thermoelectric generator containing 11 pounds of Plutonium-238.The Mars Ingenuity Helicopter was carried to Mars aboard the Perseverance rover and first flew on April 19, 2021. In its first 51 flights, Ingenuity covered 7.3 miles in over 91 minutes of flying time. The four-pound drone's two counter-rotating rotors have a four foot span. Ingenuity carries a camera and is powered by photovoltaic-charged batteries. operational: Tianwen-1 Orbiter-Lander-RoverThe Tianwen-1 mission of the China National Space Administration includes an orbiter, a lander, and a Mars rover called Zhurong. The spacecraft were launched on July 23, 2020 on a Long March V launch vehicle, and the lander/rover arrived on the Martian surface on May 14, 2021.operational: Hope Emirates Mars MissionThe Emirates Mars Mission launched an orbiter called Hope on its way to Mars atop a Japanese H-IIA launch vehicle on July 20, 2020. Hope entered Mars' orbit on February 9, 2021, and is studying weather cycles in the Martian atmosphere.operational: MAVEN: Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioNA new Mars orbiter, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) mission, was launched on November 18, 2013, atop an Atlas V-401 vehicle. MAVEN entered Martian orbit on September 22, 2014.MAVEN will attempt to determine how much of the Martian atmosphere has been lost over time by measuring the current rate of escape to space and gathering enough information about the relevant processes to allow extrapolation backward in time. MAVEN is the first Mars mission managed by the Goddard Space Flight Center. The University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics will coordinate science operations. MAVEN press kit, 2mb .pdf operational: Mars Curiosity Rover & Mars Science LaboratoryNASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission, run by JPL, was launched on Nov 26, 2011 at 10:02am EST from Cape Canaveral atop an Atlas V 541 launch vehicle.MSL rides on the "SUV-sized" Mars Curiosity rover, weighing 775kg (1700lb), and carries instruments including cameras, spectrometers, radiation detectors, and a weather monitoring station. Curiosity landed near the foot of a mountain three miles tall at 10:32pm PDT on August 5, PDT. The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter took a photo of Curiosity as it descended beneath its parachute. • MSL press kit • images & videos • mission fact sheet, ,pdf operational: Mars Reconnaissance OrbiterThe NASA-JPL Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter was launched on August 12, 2005 at 7:43am EDT, on a Lockheed-Martin Atlas V-401 launch vehicle with a Centaur upper stage. The MRO was successfully decelerated into an elliptical Mars orbit on March 10, 2006. From March until November, the MRO was aerobraked, using friction with the atmosphere of Mars to slow down into a lower, circular orbit.Since November, 2006, MRO has studied the history of water flows on Mars, and mapped the planet with HiRISE, the highest-resolution camera (1-meter) that has ever flown on a planetary mission. 2 other cameras, CTX and MARCI are also on board. Science instruments MRO carries include CRISM, a spectrometer to identify surface minerals, MCS, a radiometer to examine the atmosphere, and SHARAD sounding radar to search for water ice over one meter below the surface, and more. Because MRO is used to relay data from Mars surface probes, it is now intended to continue operating until at least the late 2020s. operational: Mars Express OrbiterMars Express, was launched on June 6, 2003, by the European Space Agency (ESA). The Mars Express orbiter carried with it a 73-lb. British lander called Beagle 2. Beagle 2 separated from Mars Express on Dec. 19, 2003, and was to land on Dec. 25th, but no signals were heard from it.The Mars Express orbiter successfully entered orbit on Dec. 25th; it is the primary vehicle of the ESA mission. ESA Multimedia Gallery operational: Mars Odyssey OrbiterAn earlier US Mars orbiter, Mars Odyssey, has relayed some of the data back from the Mars Exploration Rovers. Mars Odyssey entered Martian orbit on October 24, 2001.Odyssey maps chemical elements and minerals on the Martian surface, looks for water, and analyzes the radiation environment around Mars. shelved: ExoMars 2028?The ESA ExoMars 2022 Mission was suspended in March, 2022, due to the war in Ukraine. ExMars 2016, an eariler landing attempt, was not successful. |
Mars ImagesPhobos 2 Images has images from and a description of the Soviet Phobos 2 mission to the Martian moon in 1989. From the Russian Space Research Institute Image Processing Lab website.Hubble Space Telescope Mars Images: 1995-2007 - globe animation, 1.73 MB mpg SolarViews has a nice collection of selected Mars images, including a good rotating Mars globe animation (841 KB mpeg) created from Viking Orbiter images. It is not as sharp as the Space4Case anim (below), but the large volcanoes and some other features show up better. Mars Maps and Mars AtlasesGoogle Mars, using an interface similar to Google Earth, displays the Martian surface in visible light, infrared, and color-coded elevation maps, generated from data gathered by the Mars Global Surveyor & Mars Odyssey spacecraft. JMars, a Java-based Geographic Information System, provides the data which is displayed by Google Mars, and has additional Martian and Lunar datasets available online.The USGS Geologic Map of Mars can be downloaded at 150 dpi from the Lunar and Planetary Institute. This is a very large, 7197x5768 JPEG image, which is a 37 MB download (the page says 3.7 MB, that is an error). If you have a JPEG2000 viewer, you can download a even larger, 300 dpi image, which is a smaller file due to improved compression. US Geological Survey Mars resources include other USGS Mars maps and cut-and-paste globes. These .pdf files of maps (made with data from the Mars Global Surveyor and the Viking Orbiters), are smaller downloads. The USGS Topographic Mars Map is a printable pdf file. The USGS also provides USGS Map-a-Planet: Mars, a clickable Mars atlas. The Clickable Mars Atlas is a rotatable color globe of Mars, which you can click on to see photos of the spot where you clicked. You can also browse through a directory of named features. According to PhysOrg News, a paper in the journal Space Weather says radiation (high-energy protons) following solar flares (CMEs) might prevent any manned mars mission. Mars News has Mars news briefs, photos, and articles, plus descriptions of current and upcoming Mars spacecraft missions. Mars Daily is a similar site from Space Daily, concentrating on current news, without as much background. Explore Mars has articles and information about the planet Mars, including a Mars Database of Named Features, with basic information on over 1400 named features on Mars. The Mars Society is a non-profit independent organization dedicated to Mars exploration and settlement. Mars Spacecraft No Longer OperatingInSight, the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport spacecraft, landed on Mars on November 26, 2018, and conducted its investigations of the planet's interior until December, 2022, when it was unable to continue due to dust on its photovoltaic panels.The first of two NASA-JPL Mars Exploration Rovers, MER-A or Spirit, was launched on Tuesday, June 10, 2003, and landed safely on Mars on Jan. 3, 2004. Spirit covered about 7.7 kilometers until it became stuck on May 1, 2009; contact with that Rover was lost on March 22, 2010. The 2nd rover, MER-B or Opportunity, was launched on July 7, and landed successfully on Jan. 24. As of January, 2015, Opportunity had traveled over 40 kilometers on the Martian surface. Contact with Opportunity was permanently lost on June 10, 2018 during a dust storm on Mars. Both rovers, more capable than the earlier Mars Pathfinder (July-Sept 1997), sent back a wealth of photos and data. India's first interplanetary probe, the Mangalyaan Mars Orbiter Mission, was launched from Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh (near Chennai), atop a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), on November 5, 2013. Mangalyaan entered Mars orbit on September 24, 2014. In April, 2022, contact with Mangalyaan was permanently lost. Wikipedia: Mars Orbiter Mission NASA's Phoenix Mars Lander mission was being run by the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory at Tucson. Phoenix was launched on Saturday, August 4, 2007, and landed in the northern polar region of Mars on May 25, 2008. Phoenix carried a robotic arm which dug beneath the surface and verified the presence of water-ice in the mildly alkaline soil. Also found were small concentrations of salts, including perchlorate salt, and calcium carbonate. By November, 2008 Phoenix had ceased to function due to the cold of Martian winter. mission summary - photos Until Nov. 2006, the Mars Global Surveyor relayed some data back from the Mars Exploration Rovers. MGS entered Martian orbit in September, 1997. The spacecraft was aerobraked to a lower orbit, and began mapping the planet in March, 1999. On Nov. 2, 2006, the signal from MGS was lost. By this time about 240,000 Mars images had already been sent from MGS to Earth, including photos which suggest that running water might still occur occasionally on Mars. Russia's Phobos-Grunt (Phobos Soil) was a mission intended to return a 200 gram (7 ounce) sample of soil from the Martian moon Phobos to the Earth. The spacecraft, along with a small Chinese Mars orbiter, was launched on a Zenit-2SB41.1 rocket on Nov. 9, 2011. However, after the spacecraft reached orbit, all communications with it were lost. Phobos-Grunt at RussianSpaceWeb.com 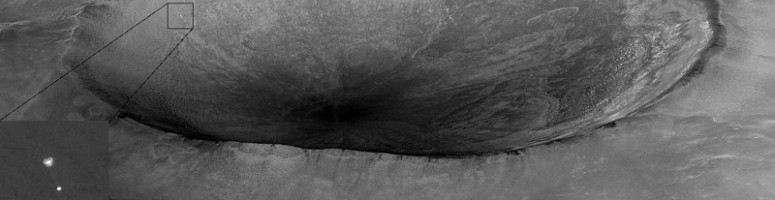 Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter saw the Phoenix Mars Lander hanging from its parachute during descent, about 20 km in front of the crater Heimdall |
Online Books about Mars, including NASA Books (NASA Special Publications)
|
Some of the books below are Adobe .pdf files, which are nice for reading materials offline. If you would like to read NASA's .html online books, like most of those below, when you are offline, you can "harvest" the pages and images for free using HTTrack, a very useful freeware website capture and offline browsing tool. HTTrack also works well with groups of .pdf files linked to from a page or directory. The Planet Mars: A History of Observation and Discovery Sheehan (1996) On Mars: Exploration of the Red Planet 1958-1978 Ezell & Ezell (1984) The Martian Landscape, NASA SP-425, 1978. Viking Orbiter Views of Mars, NASA SP-441, 1980. Basaltic Volcanism on the Terrestrial Planets (1981) Planetary Geology in the 1980s SP-467 (1985) Mars Sample Return: Issues and Recommendations commission report (1997) Humans to Mars: Fifty Years of Mission Planning, 1950-2000 Mars, Percival Lowell (1895) Is Mars Habitable? A Critical Examination of Professor Lowell's Book "Mars and Its Canals," With an Alternative Explanation Wallace (1907) over 100 NASA online books are listed on the NASA News page |